


Next: Term Enrichment
Up: Description of the search
Previous: Description of the search
The Transition Point (TP) is a frequency value that splits the vocabulary of a
text into two sets of terms (low and high frequency). This technique
is based on the Zipf Law of Word Ocurrences [10] and also on the refined
studies of Booth [1], as well as of Urbizagástegui
[9]. These
studies are meant to demonstrate that mid-frequency terms, of a text 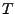 , are
closely related to the conceptual content of
, are
closely related to the conceptual content of 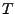 . Therefore, it is
possible to establish the hypothesis that terms closer to TP can be used as index terms of
. Therefore, it is
possible to establish the hypothesis that terms closer to TP can be used as index terms of
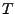 . A typical formula used to obtain
this value is:
. A typical formula used to obtain
this value is:
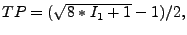 where
where 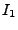 represents the number of words with frequency equal to
represents the number of words with frequency equal to 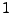 ; see
[5] [9].
; see
[5] [9].
Alternatively,
TP can be localized by identifying the lowest frequency (from the highest
frequencies) that
it is not repeated in the text; this characteristic comes from the properties of the Booth's
law of low frequency words [1]. In our experiments we have used this approach.
Let us consider a frequency-sorted vocabulary
of a document; i.e.,
![$V_{TP} = [(t_1, f_1), ..., (t_n, f_n)]$](img9.png) , with
, with
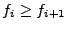 ,
then
,
then 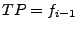 , iif
, iif 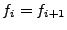 . The most important words are
those nearest to the TP, i.e.,
. The most important words are
those nearest to the TP, i.e.,
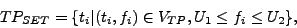 |
(1) |
where 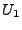 is a lower threshold obtained by a given neighbourhood
percentage of TP (NTP), thus,
is a lower threshold obtained by a given neighbourhood
percentage of TP (NTP), thus,
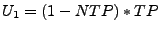 .
. 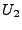 is the
upper threshold and it is calculated in a similar way (
is the
upper threshold and it is calculated in a similar way (
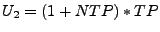 ).
Either in WebCLEF-2005 and in the current competition, we have used
).
Either in WebCLEF-2005 and in the current competition, we have used 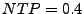 , considering that the TP technique
is language independent.
, considering that the TP technique
is language independent.



Next: Term Enrichment
Up: Description of the search
Previous: Description of the search
David Pinto
2007-05-08
![]() , with
, with
![]() ,
then
,
then ![]() , iif
, iif ![]() . The most important words are
those nearest to the TP, i.e.,
. The most important words are
those nearest to the TP, i.e.,